Understanding Stomach Cancer Treatments
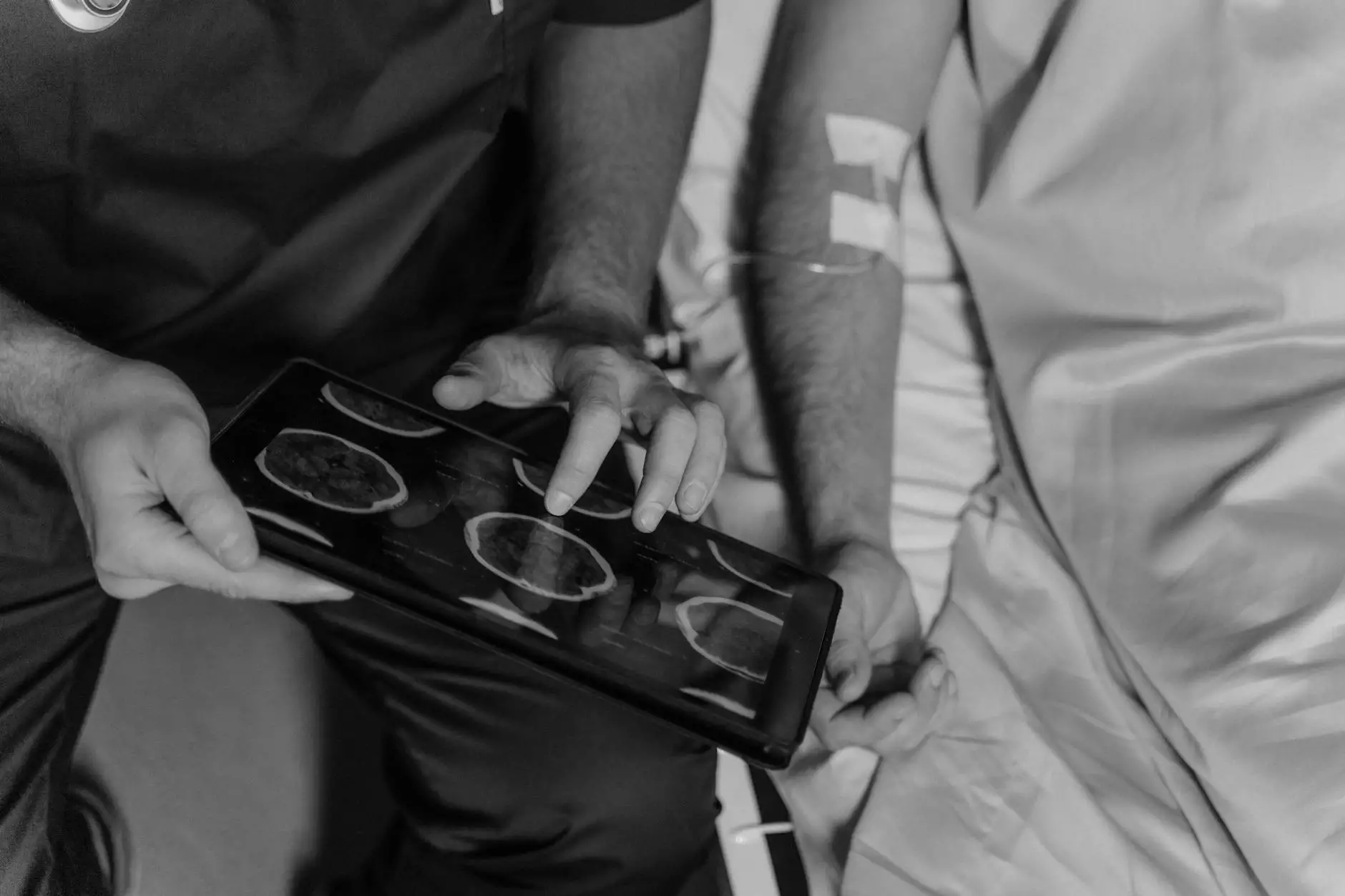
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a significant health concern globally. It affects thousands of individuals annually, making early detection and effective treatment crucial. This article delves into the comprehensive realm of stomach cancer treatments, providing in-depth knowledge about available options, advancements in medical science, and potential outcomes. For those facing this challenging diagnosis or supporting a loved one, understanding treatment pathways is vital for making informed decisions.
What is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer originates in the lining of the stomach. It can develop in various parts, including the cardia (the top part), body (middle), and pylorus (bottom part), leading to different manifestations and prognosis. This disease often goes undetected in its early stages due to non-specific symptoms, which makes awareness essential.
Recognizing Symptoms and Importance of Early Detection
The symptoms of stomach cancer can vary, and they may not appear until the disease has progressed. Some common symptoms include:
- Persistent stomach pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Difficulty swallowing
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating after meals
Early detection is key in improving treatment outcomes. Regular check-ups and an awareness of personal risk factors can contribute to early diagnosis.
Stomach Cancer Treatment Options
1. Surgical Treatments
Surgery remains one of the primary treatment options for stomach cancer, particularly in the early stages. The main surgical procedures include:
- Partial Gastrectomy: Removal of the part of the stomach containing the cancer.
- Total Gastrectomy: Complete removal of the stomach, typically required for extensive disease.
- Lymph Node Dissection: Removal of nearby lymph nodes to check for cancer spread.
Surgeons aim to eliminate as much cancer as possible while preserving healthy tissue. The choice of surgery is determined by the cancer's stage, location, and the patient's overall health.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy employs potent medications to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It is often used in conjunction with surgery or as a stand-alone treatment for advanced cases. Key points about chemotherapy in stomach cancer include:
- Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Administered before surgery to shrink tumors.
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy: Given post-surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells.
- Palliative Chemotherapy: Focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life in advanced cases.
Combining different chemotherapy drugs can enhance treatment efficacy, a tactic frequently employed by oncologists.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It may be recommended at various stages of treatment:
- Preoperative Radiation: To reduce tumor size before surgery.
- Postoperative Radiation: To eliminate residual cancer cells after surgery.
- Palliative Radiation: To alleviate pain from advanced cancer.
Advancements in technology have enabled precise targeting with radiation therapy, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are innovative treatments designed to target specific pathways that cancer cells use to grow and survive. Key targeted therapies include:
- HER2 Inhibitors: For stomach cancers that overexpress the HER2 protein, specific therapies like trastuzumab (Herceptin) may be effective.
- Anti-angiogenesis Agents: These drugs inhibit blood vessel growth in tumors, starving them of essential nutrients.
These therapies offer new hope for patients with specific genetic markers associated with aggressive disease.
5. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer treatment by enhancing the body’s natural defense mechanisms to fight cancer. Though still under research for stomach cancer, options include:
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: These medications help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
As research progresses, immunotherapy could play a more significant role in treating stomach cancer, providing hope to patients with advanced disease.
Integrating Supportive Care and Palliative Solutions
Alongside conventional treatments, a comprehensive treatment plan should include supportive care. This encompasses:
- Pain Management: Addressing pain through medication and therapies.
- Nutritional Support: Dietary guidance to maintain strength and health during treatment.
- Psychological Support: Counseling and support groups to aid emotional well-being.
Palliative care focuses on quality of life, ensuring that patients experience comfort throughout their journey.
Finding the Right Oncological Team
Choosing a qualified oncological team is paramount in navigating stomach cancer treatments. Consider the following when selecting healthcare providers:
- Experience and Specialization: Look for specialists with expertise in stomach cancer.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Ensure the team includes surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and nutritionists.
- Communication: Choose a team that values clear communication and thorough discussion of treatment options.
Collaboration among healthcare professionals often leads to more optimized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Advancements in Stomach Cancer Research and Treatment
The landscape of stomach cancer treatments is continually evolving, with research paving the way for better outcomes. Some exciting advancements include:
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on genetic testing to ensure the most effective approach.
- New Drug Discoveries: Innovative therapies are regularly being developed and tested in clinical trials.
- Combination Therapies: Studies are ongoing into the effectiveness of combining multiple treatment modalities.
Staying informed about the latest research can empower patients and families in their treatment journeys.
The Role of Support Networks
Coping with a stomach cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but support networks can play a crucial role. Engaging with family, friends, and patient support groups can provide emotional relief and practical advice. Additionally, many cancer organizations offer resources to help patients navigate their challenges.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey through stomach cancer treatments is complex yet filled with opportunities for innovation and hope. With advancements in medical science, a variety of treatment options, and the importance of a supportive care system, patients can find a personalized path forward. Staying informed and collaborating with a dedicated oncological team can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. For more information on stomach cancer and treatment options, please visit oncologicalsurgery.net.









